Integrity and Independence: Cornerstones of the Enterprise Risk Function
Introduction
As the business environment continues to evolve, the necessity for robust Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) frameworks within organizations has grown (Beasley, Clune, & Hermanson, 2005). Integral to these frameworks are the principles of independence and integrity in the risk function. Independence enables impartial risk assessment and decision-making, while integrity ensures ethical conduct and cultivates trust, both vital for effective risk management (Institute of Internal Auditors, 2017).
Understanding the Risk Function
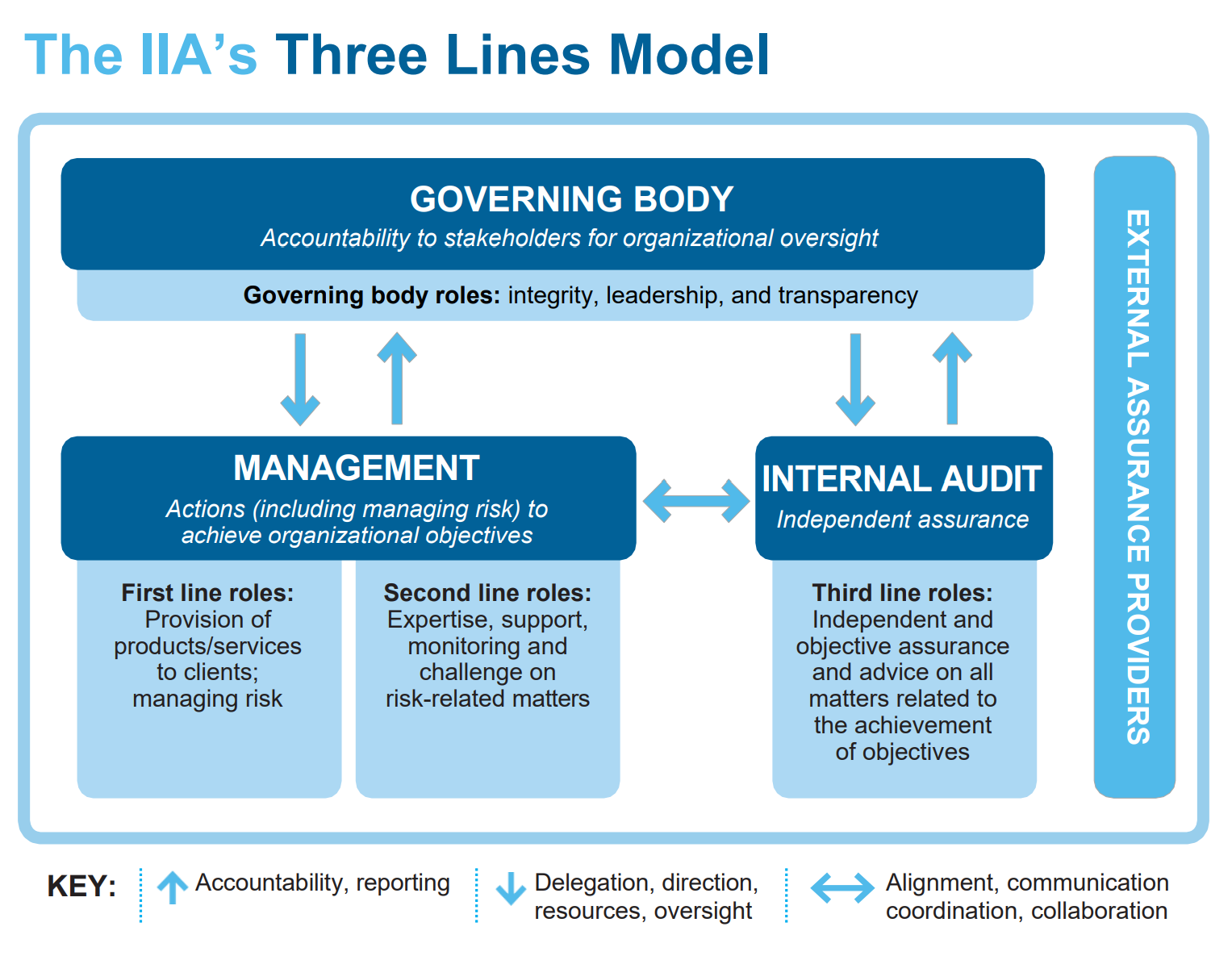
The risk function - usually embodied in a risk management department led by a Chief Risk Officer (CRO)- is responsible for identifying, assessing, managing, and monitoring enterprise risks (Nocco & Stulz, 2006). The roles of the risk function include (COSO, 2017):
- Risk Identification: Uncovering potential threats that might impede the organization's objectives.
- Risk Assessment: Determining the likelihood and potential impact of these risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing strategies to manage the identified risks.
- Risk Monitoring: Regular tracking and reporting on risk exposure and the effectiveness of risk management strategies.
Importance of Independence and Integrity in the Risk Function
Independence and integrity in the risk function are critical for several reasons:
- Objectivity: Independence allows for unbiased risk assessments, free from undue influence (Institute of Internal Auditors, 2017).
- Ethical Standards: Integrity in the risk function ensures adherence to the highest ethical standards, promoting trust and transparency (Gatzert & Martin, 2015).
- Avoidance of Conflict of Interest: Independence helps avoid conflicts where individuals or teams could be assessing risks related to their areas (Arena, Arnaboldi, & Azzone, 2010).
- Credibility: Independence and integrity enhance the credibility of risk assessments and reports for stakeholders, including regulators, shareholders, and rating agencies (KPMG, 2020).
Upholding Independence and Integrity in the Risk Function
Several measures can support the independence and integrity of the risk function:
- Culture: A culture that values risk management and recognizes the importance of an independent and integrity-driven risk function supports its autonomy and effectiveness (COSO, 2017).
- Organizational Structure: The risk function should report directly to the board or a board-level committee, ensuring high-level oversight and minimizing undue influence (ISO 31000, 2018)(COSO, 2017).
- Resources: The risk function should have adequate resources, including skilled personnel and budget, to perform its activities effectively (ISO 31000, 2018)(COSO, 2017).
- Policies and Procedures: The organization should establish clear policies and procedures outlining the responsibilities of the risk function and mechanisms to maintain its independence and integrity (Institute of Internal Auditors, 2017).
Best Practices in Maintaining Independence and Integrity
The following best practices can help maintain the independence and integrity of the risk function:
- Regular Reporting: The risk function should report regularly to the board or a relevant committee, including any threats to its independence or integrity (ISO 31000, 2018)(COSO, 2017).
- Periodic Reviews: Regular reviews, including external audits, can help ensure the risk function maintains its independence and integrity (Arena, Arnaboldi, & Azzone, 2010).
- Training and Professional Development: Continuous training and development can help risk management personnel uphold professional standards of independence and integrity (Institute of Internal Auditors, 2017).
- Collaboration and Communication: While preserving independence and integrity, the risk function should also collaborate effectively with other parts of the organization (KPMG, 2020).
Conclusion
The principles of independence and integrity in the risk function are integral components of effective ERM. They present challenges but also provide considerable benefits, including enhanced objectivity, credibility, and trust. By adopting appropriate structures, resources, and a culture conducive to these principles, organizations can uphold and maintain the independence and integrity of their risk function. This fosters effective risk management and promotes organizational success in the long term (ISO 31000, 2018)(COSO, 2017).
References
- Arena, M., Arnaboldi, M., & Azzone, G. (2010). The organizational dynamics of Enterprise Risk Management. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 35(7), 659-675.
- Beasley, M., Clune, R., & Hermanson, D. R. (2005). Enterprise risk management: An empirical analysis of factors associated with the extent of implementation. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy, 24(6), 521-531.
- COSO. (2017). Enterprise Risk Management - Integrating with Strategy and Performance. Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
- Gatzert, N., & Martin, M. (2015). Determinants and value of enterprise risk management: Empirical evidence from Germany. Risk Analysis, 35(2), 226-246.
- Institute of Internal Auditors. (2017). Independence and Objectivity: A Framework for Internal Auditors. The Institute of Internal Auditors.
- ISO 31000. (2018). Risk Management - Guidelines. International Organization for Standardization.
- KPMG. (2020). Transforming the Risk Function: Balancing Controls and Business Partnership. KPMG International.
- Nocco, B. W., & Stulz, R. M. (2006). Enterprise risk management: Theory and practice. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 18(4), 8-20.

 By
By